If you live in Florida and want a thriving vegetable garden, knowing the best time to plant is key. Planting at the right moment can make all the difference between a bountiful harvest and a disappointing patch.
Whether you’re dreaming of crisp lettuce, juicy tomatoes, or vibrant carrots, timing your garden starts can help you avoid Florida’s heat and humidity challenges. You’ll discover exactly when to plant your favorite veggies, how to choose the best varieties, and simple tips to protect your garden.
Ready to grow your best garden yet? Let’s dig into the secrets of Florida’s planting seasons.
Florida Garden Seasons
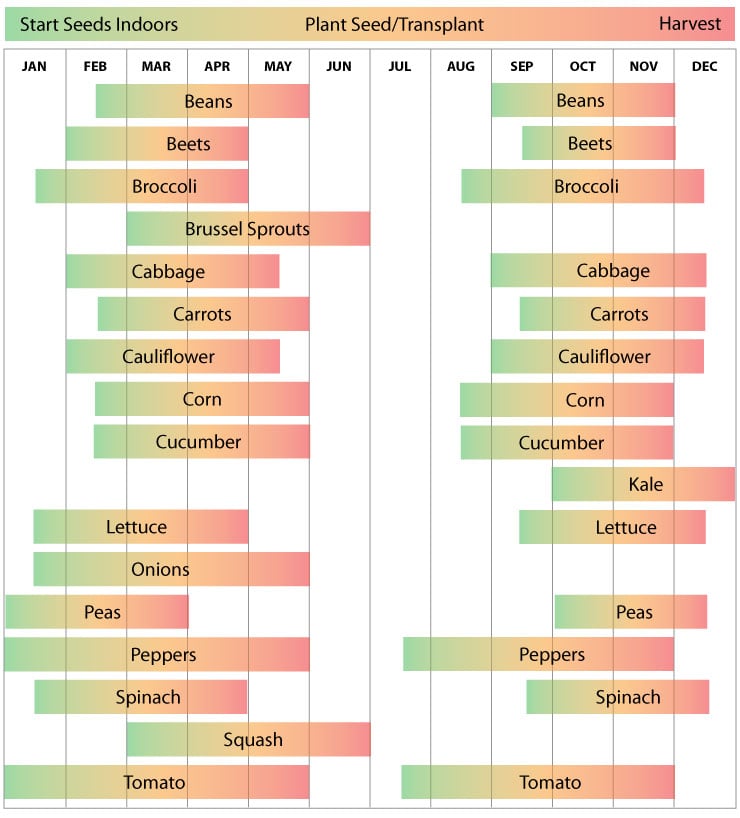
Florida’s unique climate creates distinct garden seasons that affect vegetable planting times. Understanding these seasons helps gardeners grow healthy crops year-round. Florida’s warm weather allows for multiple planting windows each year. Each season brings different challenges and advantages for vegetable gardens.
Spring Planting Window
Spring in Florida starts early with warming soil and longer days. This season suits warm-weather vegetables like tomatoes, peppers, and squash. Plant seeds or seedlings after the last frost date. Spring planting avoids the intense heat of summer. It offers a good chance for strong plant growth before summer arrives.
Fall Planting Benefits
Fall is one of the best times to plant in Florida. Cooler temperatures reduce pest problems and stress on plants. Many cool-season vegetables thrive now, such as broccoli, lettuce, carrots, and radishes. Fall planting often leads to higher yields and better flavor. Gardeners enjoy a long growing season before winter chills arrive.
Winter Gardening Tips
Winter in Florida is mild but can get chilly, especially in northern areas. Choose cold-tolerant vegetables like kale, cabbage, and spinach. Use row covers to protect plants from cold snaps. Water less often as plants grow slower. Winter gardens require less work but careful attention to frost risks.
Summer Challenges
Florida summers bring high heat, humidity, and heavy rains. These conditions can stress plants and increase pests. Plant heat-loving crops like okra and sweet potatoes. Provide shade during the hottest parts of the day. Mulch helps keep soil moist and cool. Summer gardening needs extra care to keep plants healthy.
Cool-season Crops
Cool-season crops thrive in Florida’s milder fall and winter months. These vegetables prefer cooler temperatures and can handle light frosts. Planting them at the right time ensures healthy growth and better yields. The ideal planting window usually spans from October to early January, depending on your location in Florida.
Brassicas Varieties
Brassicas include broccoli, cauliflower, cabbage, Brussels sprouts, and kale. These crops grow best in cool weather with plenty of sunlight. Starting seeds indoors before transplanting helps young plants avoid pests and harsh conditions. Planting outdoors in October gives them enough time to mature before warmer spring weather arrives.
Root Vegetables
Carrots, radishes, and beets are popular root vegetables for Florida gardens. They do well when sown directly in the soil during cool months. These crops develop sweet flavors in cooler temperatures. Space seeds properly to allow room for roots to grow. Water consistently to keep the soil moist but not soggy.
Leafy Greens
Leafy greens like lettuce, spinach, arugula, and endive flourish in Florida’s cool season. These plants grow quickly and can be harvested multiple times. They prefer well-drained soil and partial to full sun. Plant seeds or seedlings in October or November to avoid heat stress. Frequent watering supports tender, crisp leaves.
Additional Options
Onions, strawberries, and turnips also fit well into Florida’s cool-season garden. Choose short-day onion varieties suited to Florida’s climate. Strawberries can be planted in fall for a sweet spring harvest. Turnips grow fast and can be used for both roots and greens. These crops add variety and nutrition to your garden.
Warm-season Crops
Warm-season crops thrive in Florida’s hot and sunny climate. These vegetables grow best when temperatures stay warm, usually after the last frost. Starting your garden with warm-season crops can give you fresh produce all summer long. Understanding the right timing and care is key for success.
South Florida Focus
South Florida’s mild winters allow early planting of warm-season vegetables. You can plant crops like tomatoes, peppers, and beans as early as February or March. The soil warms quickly, helping seeds sprout fast. Avoid planting too late in summer to prevent heat stress on plants.
Tomato Planting Tips
Tomatoes need full sun and well-drained soil. Start seeds indoors six to eight weeks before planting outside. Transplant seedlings after the last frost date, usually in March or April. Space plants at least 18 inches apart to improve air flow. Water regularly but avoid wetting leaves to reduce disease risk.
Strawberry Season
Strawberries grow well in Florida’s warm climate. Plant strawberry runners in late fall or early winter. This timing helps plants establish roots before the hot season. Use raised beds or well-drained soil to prevent root rot. Mulch around plants to keep soil cool and moist during summer.
Credit: www.ufseeds.com
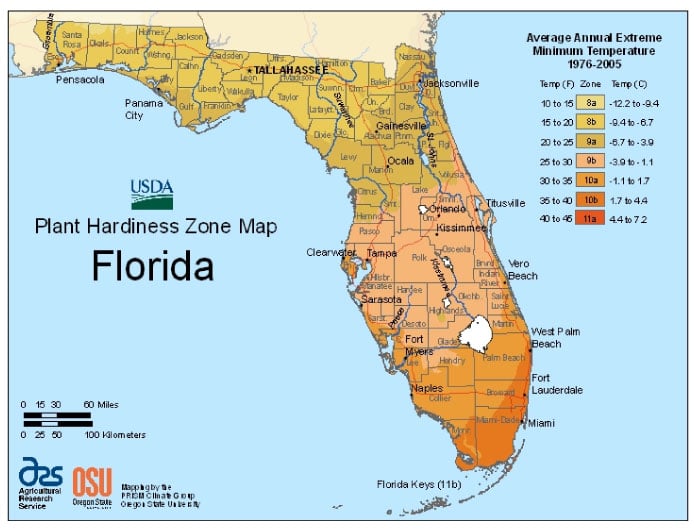
Regional Planting Differences
Florida’s climate varies widely from north to south. This affects when to plant vegetables. Understanding regional planting differences helps gardeners succeed. Each region has unique weather patterns and frost dates. Timing your garden to match these factors ensures healthy plants and better harvests.
Below are key tips for planting in North, Central, and South Florida. These guidelines help you choose the best time to start your vegetable garden.
North Florida Timing
North Florida experiences cooler winters and occasional frost. Plant cool-season vegetables by late September to early October. Crops like broccoli, lettuce, and carrots thrive in this period. Warm-season crops should be planted after the last frost in mid-April. Starting seeds indoors in early spring can give plants a strong start.
Central Florida Considerations
Central Florida has milder winters and less frost. Plant cool-season vegetables from October to February. Warm-season crops can be planted from March to May. The longer growing season allows for multiple planting cycles. Watch for sudden temperature drops and protect young plants accordingly.
South Florida Adjustments
South Florida rarely sees frost, with warm weather most of the year. Plant warm-season vegetables almost year-round. Cool-season crops grow best from November to February. Soil temperature stays higher, so some plants grow faster. Avoid planting sensitive crops during the hottest summer months to prevent heat stress.
Planting Techniques
Planting techniques play a key role in growing a healthy vegetable garden in Florida. Proper methods help seeds sprout and plants thrive despite the state’s climate challenges. Choosing the right technique depends on the vegetable and local weather conditions. Use these planting approaches to get the best start for your garden.
Starting Seeds Indoors
Starting seeds indoors protects young plants from harsh weather and pests. Use seed trays or small pots with quality seed-starting mix. Keep them warm and moist until seedlings appear. Provide enough light using a sunny window or grow lights. Harden off seedlings by gradually exposing them outdoors before planting in soil.
Direct Sowing Methods
Direct sowing means planting seeds straight into the garden soil. This works well for root crops like carrots and radishes. Make shallow furrows or holes and place seeds at recommended depths. Cover lightly with soil and water gently. Keep soil moist until seeds germinate. This method saves time and avoids transplant shock.
Protecting Seedlings
Seedlings need protection from pests, strong sun, and heavy rain. Use shade cloth or row covers to shield them. Mulch around plants to keep soil moist and reduce weeds. Check plants daily for insect damage. Organic sprays or natural predators can help control pests. Proper care ensures seedlings grow into strong, productive plants.
Pest And Disease Control
Controlling pests and diseases is vital for a healthy vegetable garden in Florida. The state’s warm climate encourages many pests and diseases to thrive. Early planning and care can reduce damage and improve harvests. Understanding common pests, using organic methods, and planting resistant varieties help maintain a strong garden.
Common Pests In Florida
Florida gardens face pests like aphids, whiteflies, and caterpillars. Spider mites and squash bugs also cause problems. These insects feed on leaves, stems, and fruits. They weaken plants and lower yields. Early detection helps stop infestations from spreading.
Organic Pest Management
Organic methods protect plants without harmful chemicals. Neem oil and insecticidal soaps control many pests. Introducing beneficial insects, such as ladybugs and lacewings, helps reduce pest numbers naturally. Crop rotation and proper spacing improve air flow and reduce pest hiding spots.
Disease-resistant Varieties
Choosing vegetable varieties bred for disease resistance saves time and effort. Resistant plants withstand common Florida diseases like fusarium wilt and powdery mildew. Seed catalogs often list disease-resistant options. Using these varieties reduces the need for sprays and treatments.
Variety Selection Tips
Selecting the right vegetable varieties is crucial for a successful garden in Florida. The state’s warm climate and unique weather patterns demand plants that can handle heat and humidity. Choosing varieties that thrive in these conditions reduces failure and boosts harvests.
Consider plants that mature quickly and resist common diseases. This approach helps gardeners avoid losses from sudden weather changes or pests. Focus on heat tolerance, short growing seasons, and disease resistance to get the best results.
Heat-tolerant Plants
Florida’s high temperatures can stress many vegetables. Heat-tolerant plants stay productive in warm weather. Examples include okra, sweet potatoes, and southern peas. These plants keep growing despite heat spikes. Planting heat-tolerant varieties prevents wilting and poor fruit development.
Look for seeds labeled as heat-resistant or suited for the South. These varieties handle Florida’s hot sun better than others. They need less water and care during heat waves, making gardening easier.
Short-season Varieties
Short-season vegetables mature faster than regular types. They finish growing before cold snaps or extreme heat arrive. This is key in Florida, where weather can shift quickly. Choose varieties that mature in 50 to 70 days for best results.
Examples include bush beans, radishes, and leaf lettuce. These plants fit well in Florida’s fall and spring growing windows. Quick harvests also free space for another crop later in the season.
Fungal Resistance
Florida’s humid climate promotes fungal diseases in gardens. Select varieties bred to resist common fungi like powdery mildew and blight. Resistant plants stay healthier and need fewer chemicals.
Tomatoes, cucumbers, and squash often suffer from fungi. Find resistant cultivars for these crops to reduce losses. Healthy plants produce better yields and reduce maintenance work.
Credit: www.ufseeds.com
Monthly Planting Guide
Planting vegetables in Florida needs careful timing. The monthly planting guide helps gardeners choose the best vegetables to plant each month. This guide focuses on the unique climate of Florida, helping you get the best harvest. Follow these monthly tips to enjoy fresh vegetables year-round.
Each month has specific vegetables that grow well. Knowing what to plant and when saves time and effort. It also reduces the risk of crop failure due to weather changes.
September Highlights
September marks the end of summer heat in Florida. It is a good time to start planting cool-season vegetables. You can plant leafy greens like lettuce and spinach. Root crops such as carrots and radishes also do well now. Start seeds indoors for broccoli and cauliflower to protect young plants. Watch for pests and use natural controls as needed.
October Planting List
October is ideal for many cool-weather crops. Plant broccoli, Brussels sprouts, and cabbage directly in the garden. Leafy greens like kale and arugula thrive this month. Root vegetables including beets and turnips grow strong now. In South Florida, start warm-weather crops like strawberries. Direct sow seeds for fast growth. Use shade cloth to protect young plants from sun and pests.
November And Beyond
November brings cooler temperatures perfect for cool-season crops. Continue planting leafy greens and brassicas. Onions and garlic can be planted for spring harvest. Prepare soil for winter crops by adding compost. In South Florida, you can still plant some warm-season vegetables. Keep watering regularly and watch for frost in North Florida. Plan for succession planting to keep your garden producing.

Credit: www.revivalgardening.com
Frequently Asked Questions
What Month To Plant Vegetables In Florida?
Plant cool-season vegetables in Florida from October to December. Warm-season crops grow best from February to April. South Florida allows year-round planting.
What Can I Plant In October In Florida?
In October, plant cool-season vegetables in Florida like broccoli, lettuce, carrots, radishes, kale, cauliflower, and cabbage. South Florida can also start warm-weather crops and strawberries. Start seeds indoors for brassicas or sow root vegetables directly in the garden.
Can I Plant Tomatoes In September In Florida?
Yes, plant tomatoes in early September in Florida for a fall harvest. Choose heat-tolerant, disease-resistant varieties.
Is September Too Late To Plant A Garden?
September is not too late to plant a garden, especially in warmer climates. Plant heat-tolerant or cool-season crops early in the month for best results.
Conclusion
Planting your vegetable garden at the right time helps plants grow strong. Florida’s warm climate lets you start many vegetables in fall or spring. Choose cool-season crops like broccoli and lettuce in October for best results. South Florida gardeners can also try warm-weather plants early.
Starting seeds indoors protects young plants from pests. Watch the weather and protect crops as needed. With simple care and timing, your garden will thrive. Happy planting and enjoy fresh vegetables all year!

