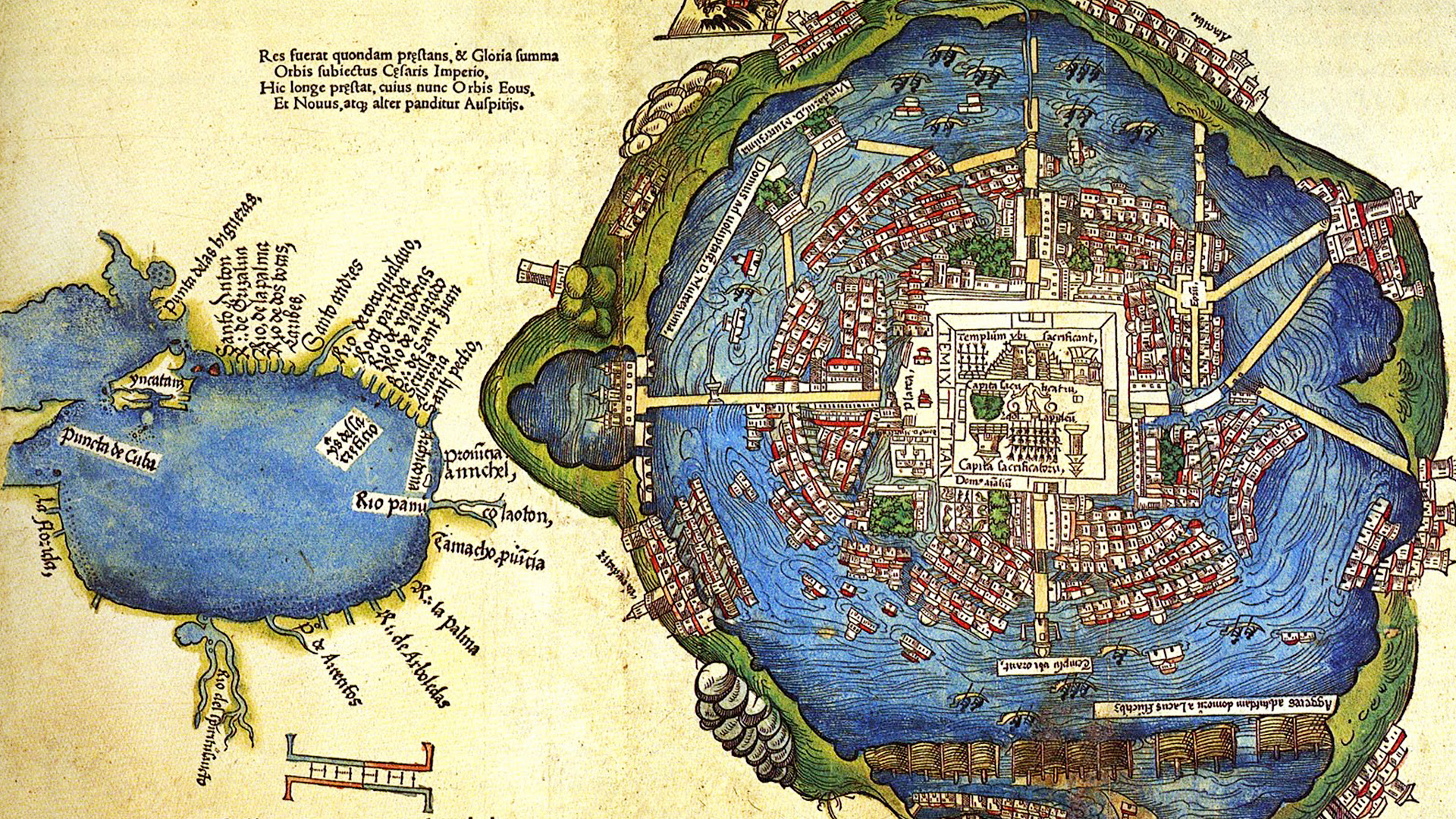
Imagine standing on the shores of a sparkling lake, where vibrant gardens float effortlessly on the water’s surface. This isn’t a scene from a fairytale, but a breathtaking reality crafted by the Aztecs on Lake Texcoco.
These ancient gardens, known as chinampas, were a marvel of agricultural innovation and are still studied for their ingenuity today. But why should you care about gardens that existed centuries ago? Because understanding these floating masterpieces might just unlock secrets that could transform the way you think about sustainable living and food production.
Intrigued? Let’s dive into the fascinating world of the Aztecs’ floating gardens and discover how they could inspire solutions for modern challenges.
JUMP TO TOPIC
Origins Of Lake Texcoco Gardens
The Aztecs were not just fierce warriors; they were skilled architects. Their ability to create gardens on Lake Texcoco shows their engineering brilliance. These gardens, known as chinampas, were artificial islands. They supported agriculture and sustained their growing population. Let’s explore how these gardens came to be.
Historical Context
Lake Texcoco was central to Aztec civilization. The Aztecs settled in the region around the 14th century. They needed innovative solutions to feed their people. The lake’s marshy terrain was challenging for traditional farming. So, the Aztecs engineered chinampas, transforming the landscape. These floating gardens became vital for their survival.
Geographic Significance
Located in the Valley of Mexico, Lake Texcoco had strategic importance. Its location offered natural protection from invaders. The lake’s waters provided resources for irrigation. Its fertile soil was perfect for farming. The Aztecs used this to their advantage. By building gardens on the lake, they expanded their agricultural land. This helped sustain their empire.

Credit: www.youtube.com
Engineering Techniques
The engineering techniques of the Aztecs were truly remarkable. They created floating gardens on Lake Texcoco. These gardens, known as chinampas, showcased their advanced engineering skills. The Aztecs transformed a watery landscape into fertile farmland. Their methods were sustainable and efficient. Let’s explore the design principles and construction materials they used.
Design Principles
The Aztecs designed chinampas with precision. Each garden was rectangular and surrounded by canals. This layout ensured efficient water management. The canals provided easy access for irrigation. They helped transport crops and materials. The Aztecs used a grid-like system. This maximized space and allowed for crop rotation. Each chinampa was about 300 feet long and 30 feet wide. This size allowed for diverse planting. The design was both practical and adaptable.
Construction Materials
The Aztecs used natural materials for their gardens. They constructed chinampas with layers of mud and vegetation. Reeds and sticks were woven together to form a base. This base floated on the lake surface. It provided stability and structure. Mud was piled on top to create a fertile layer. The Aztecs used aquatic plants to bind the soil. These plants enriched the soil with nutrients. Willow trees were planted at the edges. Their roots anchored the chinampas in place. These materials were abundant and sustainable.
Agricultural Practices
The Aztecs were masters of innovative farming techniques. They transformed Lake Texcoco into fertile gardens known as chinampas. These floating gardens supported a thriving civilization. Their agricultural practices ensured food security and cultural prosperity.
Crop Varieties
Aztecs cultivated diverse crops in their gardens. Maize was a staple in their diet. They also grew beans, tomatoes, and chili peppers. These crops provided essential nutrients for their community. The selection of crops was strategic. It ensured a balanced diet and sustained their society.
Irrigation Methods
The irrigation system was advanced. They used canals to supply water to chinampas. This ensured crops had sufficient moisture. It improved crop yield and quality. The Aztecs understood the importance of water management. Their methods optimized agricultural productivity and efficiency.

Credit: en.wikipedia.org
Cultural And Societal Impact
The Aztec gardens on Lake Texcoco showcase impressive agricultural innovation. These floating gardens, or chinampas, supported large populations. They highlight the Aztecs’ harmony with nature, influencing modern sustainable farming practices.
The Aztecs were known for their ingenuity and their ability to adapt to their environment. Their floating gardens, or chinampas, on Lake Texcoco are prime examples. These gardens were not just an agricultural triumph but a cultural cornerstone. They impacted Aztec society and continue to influence modern gardening practices.Role In Aztec Society
The chinampas played a crucial role in the daily lives of the Aztecs. They were more than just a means of food production. They were central to the community’s social structure. Imagine walking through a vibrant garden that provides food and medicine. This was the reality for the Aztecs. These gardens supported a thriving population by supplying essential crops such as maize, beans, and squash. The Aztecs also held religious ceremonies in these spaces. They celebrated the bounty of their land and honored their gods. The gardens were a testament to their resourcefulness and deep spiritual connection to nature.Influence On Modern Gardening
You might find echoes of chinampa techniques in today’s sustainable gardening practices. Raised beds and hydroponics are reminiscent of Aztec methods. These modern techniques often aim for efficiency and sustainability. Some urban gardeners have adopted similar methods to maximize limited space. In cities, rooftop gardens mirror the resourcefulness of the Aztecs. They offer a green oasis in concrete jungles, much like chinampas did in the bustling Aztec capital. Have you ever considered how your garden could benefit from ancient wisdom? The Aztecs’ innovative approach to gardening teaches us to work with our environment. It’s a lesson in creativity and adaptability that still resonates today. The cultural and societal impact of the Aztec chinampas extends beyond their time. They continue to inspire and challenge us to think differently about how we grow our food. What lessons will you take from their legacy to apply to your own gardening practices?Environmental Adaptations
The Aztecs were brilliant at adapting to challenging environments. Their gardens on Lake Texcoco are a testament to their ingenuity. They transformed floating islands into fertile land. This innovation supported their vast empire. Let’s explore how they achieved environmental harmony.
Sustainability Measures
The Aztecs practiced sustainable farming. They used chinampas, which are floating gardens. These gardens were made from mud and reeds. They provided a rich soil for crops. This method allowed continuous harvests year-round. The Aztecs rotated crops to maintain soil health. They even used human waste as fertilizer. This minimized waste and enriched the soil.
Challenges Overcome
Building gardens on a lake was not easy. The Aztecs faced flooding and soil erosion. They created canals to manage water flow. These canals prevented flooding during rainy seasons. They also used barriers to protect the chinampas. These barriers stopped soil from washing away. The Aztecs adapted to changing water levels. Their techniques ensured the gardens remained productive.
Credit: www.vision.org
Legacy And Preservation
Aztec gardens on Lake Texcoco showcased incredible engineering and artistry. Floating platforms supported lush vegetation, creating vibrant ecosystems. These gardens highlight the Aztecs’ innovative spirit and dedication to preserving nature’s beauty.
The Aztec gardens built on Lake Texcoco, known as chinampas, represent a stunning blend of innovation and natural beauty. These floating gardens are a testament to the ingenuity of the Aztec civilization. They not only provided food but also supported biodiversity. Yet, their true wonder lies in their legacy and the efforts to preserve them today. How can these ancient practices inspire sustainable gardening in our modern world?Archaeological Discoveries
Recent archaeological findings have shed light on the complex network of these gardens. Scientists have discovered remnants of the chinampas, revealing their intricate design and construction. This discovery includes canals and raised beds that were used to cultivate a variety of crops. These findings not only highlight Aztec engineering skills but also offer insights into sustainable agriculture. Imagine walking through a modern city and stumbling upon an ancient blueprint of environmental harmony.Efforts To Protect
Today, there is a growing movement to protect these historical wonders. Conservationists and local communities are working together to restore and maintain the chinampas. This involves cleaning canals, planting native vegetation, and promoting eco-tourism. By doing so, they aim to preserve the cultural heritage and ecological significance of the area. What role can you play in supporting these efforts? Engaging with these initiatives can be as simple as visiting the site, learning more, or even advocating for sustainable practices in your community. The preservation of the chinampas is not just about saving the past; it’s about learning from it. How can these ancient techniques inspire your own gardening or sustainability projects?Frequently Asked Questions
What Was Built On Lake Texcoco?
The Aztecs built Tenochtitlan on Lake Texcoco. This city became the heart of the Aztec Empire. Today, Mexico City stands where Tenochtitlan once was.
What Were The Aztec Gardens Called?
Aztec gardens were called “chinampas. ” These floating gardens were built on shallow lake beds and used for agriculture. Chinampas provided fertile land for crops and were a vital part of Aztec farming techniques, showcasing their innovative agricultural practices.
What Were Aztec Farmers Constructed Soil Islands In Lake Texcoco Called?
Aztec farmers constructed soil islands in Lake Texcoco called “chinampas. ” These floating gardens enhanced agricultural productivity. Chinampas allowed year-round farming and were highly efficient. Aztecs ingeniously used them to maximize land use and food production. These islands contributed significantly to the Aztec Empire’s agricultural success.
Why Did The Aztecs Built Floating Gardens?
The Aztecs built floating gardens, or chinampas, to maximize agricultural space in the swampy regions of Lake Texcoco. These gardens provided fertile land for crops, ensuring food supply and supporting their growing population. This innovative method allowed efficient use of limited land resources, enhancing agricultural productivity.
Conclusion
The Aztecs showed true innovation with their floating gardens. These gardens on Lake Texcoco were a marvel. They thrived on water, not land. This method provided food and supported their community. It demonstrated human creativity and resilience. Today, these gardens inspire modern sustainable practices.
They remind us of nature’s power and human ingenuity. Studying them can teach us about sustainable living. Their legacy continues to influence our world today. A true testament to ancient wisdom and environmental harmony.

